45 coupon collector problem in r
PDF Using Stirling numbers to solve coupon collector problems Marko R. Riedel March 13, 2019 The coupon collector problem has been studied in many variations, from ba-sic probability to advanced research. For an introduction consult the Wikipedia ... This was math.stackexchange.com problem 2426510. 2.1 Drawing coupons until at least 2 instances of each type An R implementation of the "Coupon Collector's Problem? I saw this question on r/askscience and was intrigued. The expectation is 236 days (52 * H_52) with a standard deviation of sqrt((pi 2 / 6)*52 2) = 67. However, I wanted to try a stochastic approach in R.
The Weighted Coupon Collector's Problem and Applications Abstract In the classical coupon collector's problem n coupons are given. In every step one of the n coupons is drawn uniformly at random (with replacement) and the goal is to obtain a copy of all the coupons. It is a well-known fact that in expectation n \sum_ {k=1}^n 1/k \approx n \ln n steps are needed to obtain all coupons.

Coupon collector problem in r
r-simulations/CouponCollector.md at master · havanagrawal/r-simulations coupon_collector_simulation = function ( n) { collected_coupons <- c () attempts <- 0 while (length ( collected_coupons) != n) { # Generate a new coupon uniformly from 1 to n new_coupon <- sample ( n, 1 ) # Add it to the set of coupons we have collected_coupons <- unique (c ( collected_coupons, new_coupon )) attempts <- attempts + 1 } attempts } Solved 5: Coupon collector's problem From Wikipedia, the | Chegg.com 5: Coupon collector's problem From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. In probability theory, the coupon collector's problem describes "collect all coupons and win" contests. It asks the following question: If each box of a brand of cereals contains a coupon, and there are n different types of coupons, what is the probability that more ... R Program That Draw Histogram of Coupon's Collector Problem R Program That Draw Histogram of Coupon's Collector Problem Raw coupon.R random.int <- function ( n) { sample.int ( n, 1) } random.coupon <- function ( ...) { count <- 0 have.coupon <- logical ( ...) while (! all ( have.coupon )) { have.coupon [random.int ( ... )] <- TRUE count <- count + 1 } count } sample.coupon <- function ( n, size=10*n) {
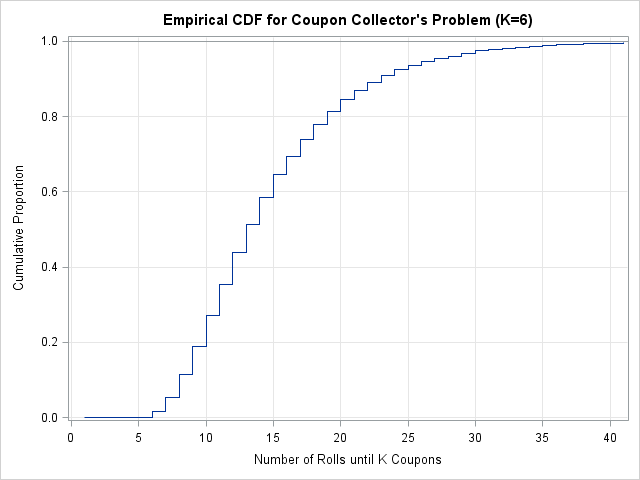
Coupon collector problem in r. Simulating the Coupon Collector's Problem - The DO Loop I want the simulation to work for the coupon collector's problem with K coupons, so I'll use a little probability theory. You can look up formulas for the mean and variance of the survival time as a function of K. For my simulation, I will use L = mean + 2*StdDev as the maximum number of rolls in each trial. When K =6, L is 41. Collecting k Complete Sets of Coupons - MathPages To summarize, if there are n different kinds of coupons, let E_n (k) denote the expected number of purchases necessary to acquire k complete sets. The well-known case is with k=1, in which case we have E_n (1) = n (1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + ... + 1/n) for all n. Of course, the case of n=1 trivially gives E_1 (k) = k for all k. Expected Number of Trials until Success - GeeksforGeeks Proof: Let R be a random variable that indicates number of trials until success. The expected value of R is sum of following infinite series E[R] = 1*p + 2*(1-p) ... Coupon Collector Problem 1: Suppose there are n types of coupons in a lottery and each lot contains one coupon (with probability 1 = n each). How many lots have to be bought (in ... PDF Lecture 6: Coupon Collector's problem The Coupon Collector's problem There arendistinct coupons and at each trial a coupon ischosen uniformly at random, independently of previoustrials. Letmthe number of trials. Goal: establish relationships between the numbermoftrials and the probability of having chosen each one ofthencoupons at least once.
Coupon collector's problem - Wikipedia Donald J. Newman and Lawrence Shepp gave a generalization of the coupon collector's problem when m copies of each coupon need to be collected. Let Tm be the first time m copies of each coupon are collected. They showed that the expectation in this case satisfies: Here m is fixed. When m = 1 we get the earlier formula for the expectation. (PDF) A note on the coupon - collector's problem with multiple arrivals ... The coupon-collector's problem is a classical problem in combinatorial prob-. ability. The description of the basic problem is easy: consider one person. that collects coupons and assum e that ... PDF Math 365 Coupon Collector's Problem 1 Coupon Collector's Problem ... Math 365 Coupon Collector's Problem Submit your R script to tleise@amherst.edu by next Tuesday (a handwritten submission is also nefor this lab). The objective of this lab is to study a famous problem in probability, thecoupon collector's problem,and its connection to Poisson processes. 贈券收集問題 - 维基百科,自由的百科全书 贈券收集問題(Coupon collector's problem) 是機率論中的著名題目,其目的在解答以下問題: . 假設有n種贈券,每種贈券獲取機率相同,而且贈券亦無限供應。 若取贈券t張,能集齊n種贈券的機率多少?. 計算得出,平均需要 (()) 次才能集齊n種贈券——这就是赠券收集问题的时间复杂度。
The Coupon-Collector Problem Revisited - Purdue University The Coupon-CollectorProblem Revisited Arnon Boneh and Micha Hofri Computer Sciences Department Purdue University West Lafayette, IN 47907 CSD-TR-952 February, 1990 THE COUPON-COLLECTORPROBLEM REVISITED Amon Boneh- IOE Department, University ofMichigan, Ann Arbor MI 48109-2177 Micha Hofrit - Department ofComputer Science, The Technion-ITT,Haifa Help with Coupon Collector's Problem : R_Programming - reddit Hi, I'm struggling with a script in R to simulate the coupon collector's problem. Any help would be greatly appreciated! Here's the exercise: Write a function coupon(n) for simulating the coupon collector's problem. That is, let X be the number of draws required to obtain all n items when sampling with replacement. Inverse Coupon Collector's Problem - Rebecca's Home Page The Inverse Coupon Collector's Problem can be stated as follows: For fixed i, m, what value of N maximizes the probability p ( i, m; N )? That is, given i, m, what is the most likely value of N in... PDF 7. The Coupon Collector Problem - UNIVPM 1. In the coupon collector experiment, run the experiment in single-step mode a few times for selectedvalues of the parameters. The Probability Density Function Now let's find the distribution of Wm,k. The results of the previous section will be very helpful 2. Argue that Wm,k =n if and only if Vm,n−1=k− 1 and Vm,n =k.
Coupon Collector Problem Code - MathWorks I've been trying to create a program to calculate the mean time taken to collect all coupons in the coupon collector problem. It is known that the expected time to do this is roughly n*log(n). Through just general trials with large numbers of repeats, my answer for E(T) never seems to be n*log(n) and I can't figure out why.
Coupon Collector Problem - Words and Mappings | Coursera Join for free Coupon Collector Problem Analysis of Algorithms Princeton University 4.5 (152 ratings) | 67K Students Enrolled Enroll for Free This Course Video Transcript This course teaches a calculus that enables precise quantitative predictions of large combinatorial structures.
Coupon Collector Problem - Words and Mappings | Coursera It's a well known phenomenon that has lots of applications. And that's the combinatorics of the coupon collector problem. There is a combinatorial concept called a surjection that does really need analytic combinatorics to study. So what we call a coupon collector sequence is, it's an M-word with no empty set. So that's called an M-surjection.
Coupon Collecting Problem using Inclusion-Exclusion Coupon collector problem Incorrect recurrence solution. 0. Coupon collecting with unequal probabilities (S.Ross Min-Max approach) 1. Probability distribution in the subset version of the coupon collector's problem. 6. Modified coupon collector's problem, where you can trade off excess coupons. 10.
The Coupon Collector's Problem - YouTube Get 2 months of skillshare premium here! my discord server! coupon collector's problem goes as foll...
PDF Tighter bound for Coupon Collector using Union Bound Tighter bound for Coupon Collector using Union Bound Since the bounds that we obtain from Markov and Chebyshev for Coupon Collector are not "tight", we will now use the Union bound to get better results. Let Er i be the event that we have not yet obtained coupon ieven after rtrials. Then, Pr[Er i] = 1 1 n r e r n (1) We used the identity 1 + t ...
PDF MATerials MATemàtics 2 - Departament de Matemàtiques The history of the coupon collector's problem began in 1708, when the problemfirstappearedinDeMensuraSortis(OntheMeasurementofChance) written by A. De Moivre. More results, due among others to Laplace and Euler(see[8]foracomprehensiveintroductiononthistopic),wereobtained inthecaseofconstantprobabilities,i.e. whenp k 1 N foranyk.
(PDF) Solution of the inverse coupon collector's problem The classic coupon collector's problem states that: Given that there . are N different coupons available in boxes of a certain product, what .
Coupon Collector's Problem - Amherst College Clearly X 1 = 1. On each draw, the probability of collecting a new coupon, given that we already have k − 1 different coupons, is p k = N − ( k − 1) N. That is, X k follows a geometric distribution and E ( X k) = 1 p k = N N − k + 1.
PDF Collecting coupons — A mathematical approach - ed This situation is sometimes known as the "coupon collector's problem" or"cereal box problem" (since the coupons are often a set of toys found in apacket of cereal) and the aim here is to analyse it generally and then demon-strate by using specific examples. It provides a most interesting instance ofhow mathematics can be used to analys...
R Program That Draw Histogram of Coupon's Collector Problem R Program That Draw Histogram of Coupon's Collector Problem Raw coupon.R random.int <- function ( n) { sample.int ( n, 1) } random.coupon <- function ( ...) { count <- 0 have.coupon <- logical ( ...) while (! all ( have.coupon )) { have.coupon [random.int ( ... )] <- TRUE count <- count + 1 } count } sample.coupon <- function ( n, size=10*n) {
Solved 5: Coupon collector's problem From Wikipedia, the | Chegg.com 5: Coupon collector's problem From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. In probability theory, the coupon collector's problem describes "collect all coupons and win" contests. It asks the following question: If each box of a brand of cereals contains a coupon, and there are n different types of coupons, what is the probability that more ...
r-simulations/CouponCollector.md at master · havanagrawal/r-simulations coupon_collector_simulation = function ( n) { collected_coupons <- c () attempts <- 0 while (length ( collected_coupons) != n) { # Generate a new coupon uniformly from 1 to n new_coupon <- sample ( n, 1 ) # Add it to the set of coupons we have collected_coupons <- unique (c ( collected_coupons, new_coupon )) attempts <- attempts + 1 } attempts }









Post a Comment for "45 coupon collector problem in r"